
A block, also known as a substrate of p-type semiconductor acts as the base for MOSFET.To understand how FET work, we’ll take a look at a typical circuit diagram as follows: MOSFET Diagram With its different pin construction, it works slightly differently as compared to BJTs. What is FET and How does it work?įield-Effect Transistor, the other type of transistor, is most commonly classified as MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) and is constructed with pins Gate, source, drain. Additionally, instead of emitting electrons, the emitter in a PNP emits “holes” (a conceptual absence of electrons), which are then collected by the collector.
Essentially, current flow is still controlled by the base but flows in the opposite direction. Whereas for a PNP transistor, it consists of a layer of N-doped semiconductor between two layers of P-doped material, where the base current entering into the collector is amplified. The emitted electrons are finally collected by the collector and sent to the following part of a circuit. The emitter then “emits” electrons into the base, with the base controlling the no. Now that we’ve defined what are BJTs, we’ll take a look at how BJTs work with a simple illustration below: Refįor an NPN transistor, it consists of a layer of P-doped semiconductor between two layers of N-doped material, where electrons are passed from the emitter to the collector instead.

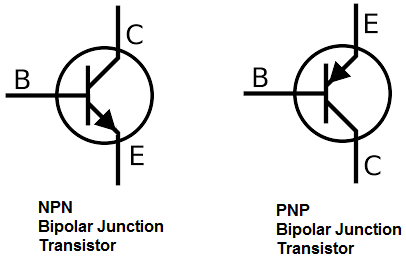
The difference between the two can be spotted with the arrow direction where for NPN, the arrow’s exiting the base while for PNP, the arrow’s entering the base. Firstly, for BJTs, it comes in two iterations or versions NPN and PNP BJT, with its circuit symbols as shown below: BJTs: NPN vs PNP circuit symbolsĪs you can see, both NPN and PNP iterations have pins labeled Collector (C), Base (B), and emitter (E).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
